Smart Irrigation District Supervision System
- Overview
- Main Features
- Main Indicators
- Main functions
- Device Configuration
The smart irrigation area information platform uses advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things, the Internet, cloud computing, and big data analysis to obtain real-time and accurate information on water and rainfall conditions, soil moisture conditions, channel water levels, channel flow, pump station operating status, gate operating status, on-site video, and other information. It processes the collected data to achieve real-time sharing of information resources in the irrigation area, improve the operational efficiency of the irrigation area, and reduce operational costs. It provides scientific decision-making basis for the irrigation area management department, ultimately achieving informatization of irrigation area management, rational allocation of water, precise measurement of water, automation of control, and standardization of charging, providing technical support for efficient modern agriculture.
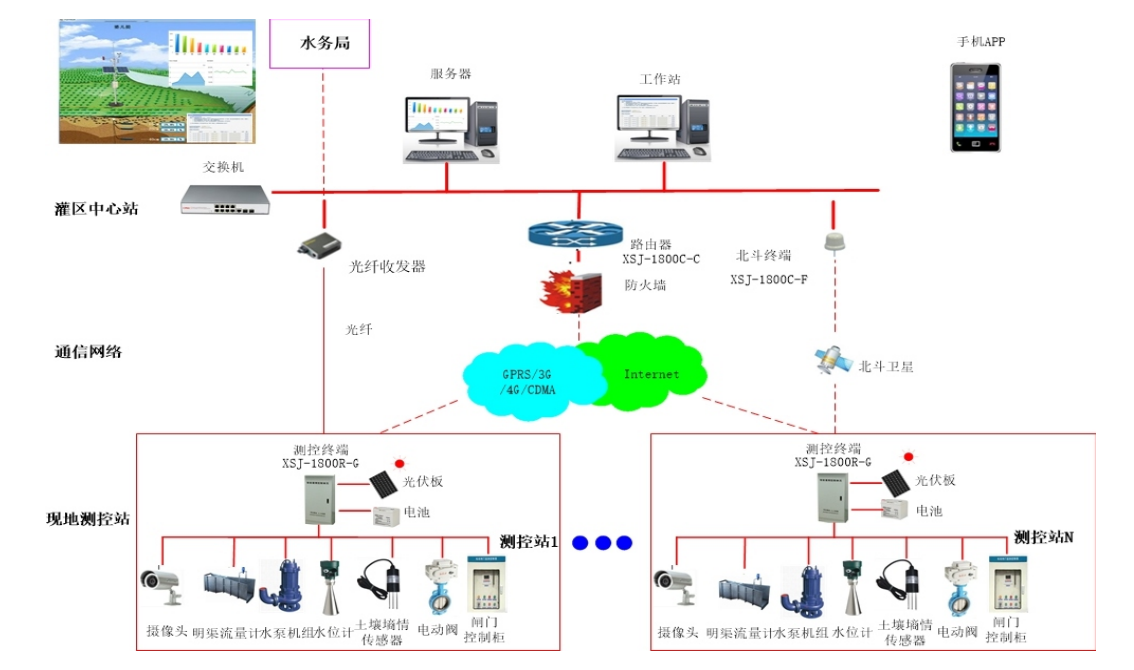
Smart Irrigation Area Supervision System Network Diagram
Typical Project: Guangxi Zhaoping Zhoujia Irrigation Area Agricultural Water Price Reform Project - Gates, Water Measurement Facilities and Equipment
Project Overview: The comprehensive reform project of agricultural water prices in the Zhoujia irrigation area of Zhaoping County is located in the Zhoujia irrigation area of Zhaoping County, Guangxi. The irrigation area was originally designed to irrigate 14,000 acres, with an effective irrigation area of 9,500 acres. Due to the requisition of part of the irrigation area of the North Canal, the planned irrigation area for this implementation scheme is 11,300 acres, including 9,040 acres of rice, 1,469 acres of citrus, and 790 acres of other crops. It involves villages such as Huangyao Street Village, Bengjiang Village, Gongqiao Village, Bitou Village, Jianpan Village, Zhongdong Village, Xinzai Village, Baishan Village, Chunfu Village in Huangyao Town, and Jiatian Village in Zhangmulian Township.The work mainly involves: the construction of 49 new gate control points, 3 sets of precise integrated gates, 16 sets of conventional integrated gates, 30 sets of manual gates, 91 sets of water measurement facilities, 4 Doppler monitoring points, 46 rectangular weir monitoring points, and 41 standard cross-sections + water level gauge monitoring points. One centralized control center.
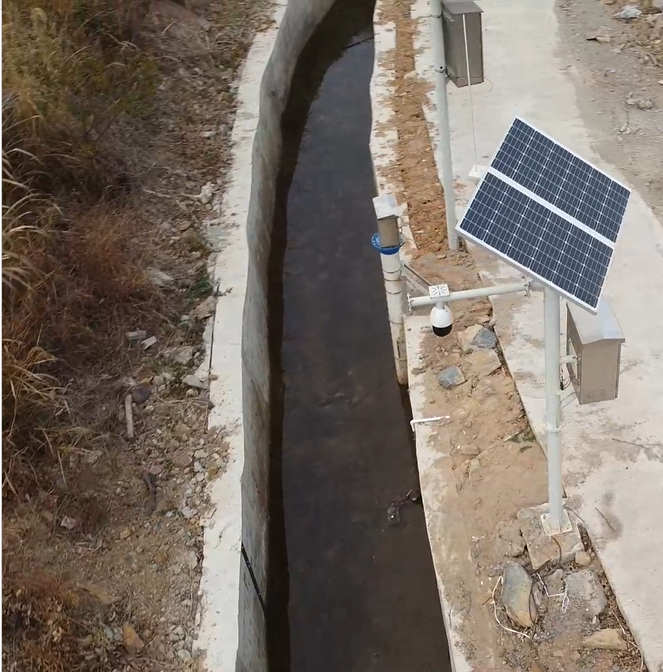

1) The central station of the irrigation area can communicate through the Internet to perform highly reliable and safe operational control of equipment such as water pumps and gates at various irrigation stations. The system software is powerful, and the human-machine interface is user-friendly, allowing comprehensive monitoring of the operational status of each water pump, gate, and canal, making it very convenient to use and reducing the need for personnel to manage on-site.
2) The system follows design principles of safety and reliability, advanced technology, easy expansion, and convenient operational management. It is simple and easy to operate, with low user costs, allowing users to quickly use and manage the system after simple training, effectively meeting the needs for agricultural water-saving irrigation monitoring and management.
3) The performance of the measurement and control terminal station equipment is stable, with high precision and strong real-time capabilities, allowing for reliable remote control.
4) The measurement and control terminal station is powered by solar energy and batteries, and is designed to be resistant to lightning, rain, dust, theft, and extreme temperatures, making it reliable for use in harsh outdoor environments.
5) The system supports various communication methods such as GPRS, 3G, and wireless data transmission stations, facilitating user external interfaces and applications.
1) Operating environment parameters
Irrigation area central station: Temperature: 5~40℃, allowable relative humidity: ≤90% (40℃)
Measurement and control terminal station: Temperature: -25~55℃, allowable relative humidity: ≤95% (40℃)
2) Parameter measurement error: ≤±1% (depends on the selected collection sensor)
3) Control accuracy: 100%
4) Electrical quantity collection cycle: ≤2s
5) Non-electrical analog quantity collection cycle: ≤2s
6) Status and alarm point collection cycle: ≤100ms
7) Event record resolution time: ≤2ms
8) Data transmission time of changes collected by the measurement and control station to the real-time database: ≤2s
9) Response time for the measurement and control station to accept control commands: ≤1s
10) Response time for calling a new screen: ≤1s
11) Dynamic data refresh time on the displayed screen: ≤2s
12) Response time for main control level control function: ≤1s
13) Time from alarm or incident occurrence to sound output on the screen: ≤2s
14) System availability: ≥99.9%
15) Mean time between failures (MTBF): 50000 hours
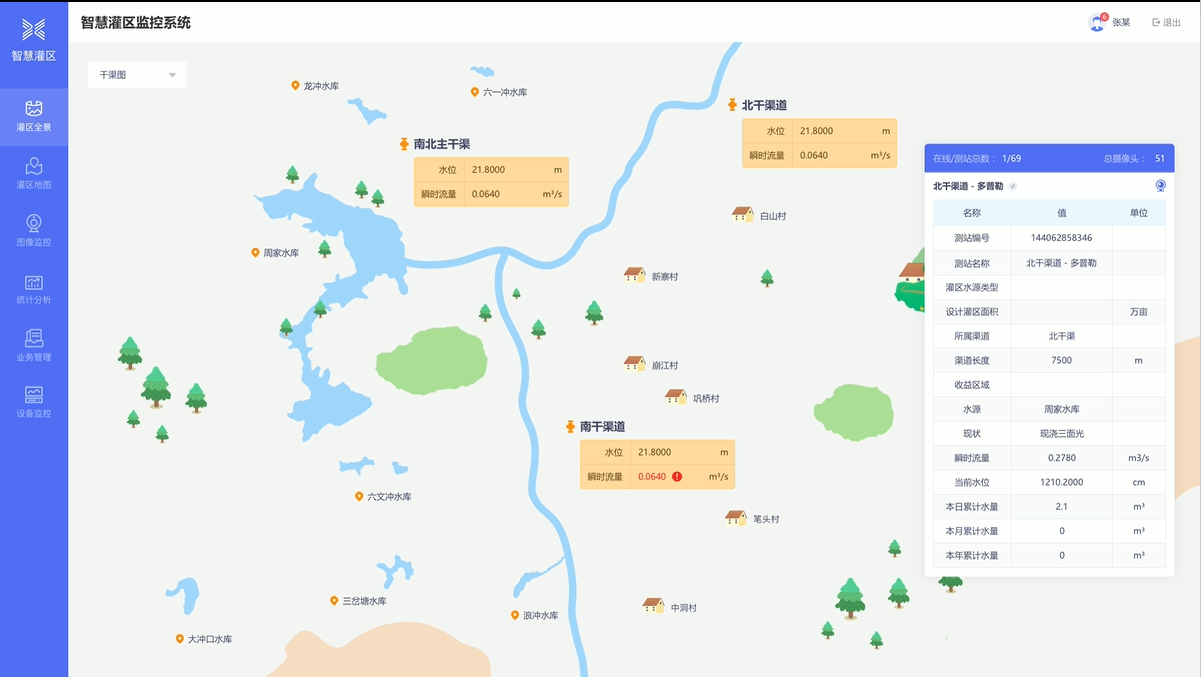
1) Irrigation District Map Information
Using the GIS geographic information system, it is very convenient to query and browse the geographical location information, meteorological information, key operating parameters, equipment information, etc. of each irrigation district's measurement and control stations. The system supports flat maps, terrain maps, original maps, and three-dimensional maps, which can be switched for use.
2) Real-time Data Monitoring
Real-time collection of operating parameters, equipment parameters, meteorological information, and status parameters from each measurement and control station, mainly including instantaneous flow, cumulative flow, water level, gate position, soil moisture content, rainfall, terminal voltage, gate status, communication status, environmental temperature, humidity, sunlight, wind force, and other real-time data monitoring of main canals, branch canals, and ditches.
3) Remote Monitoring of Measurement Stations
Through the system, remote operation or monitoring of the pump stations or gates of each irrigation district can be achieved, including remote operation of equipment and parameter settings.
4) Video Remote Monitoring
Through the central station intelligent monitoring system, video monitoring of various equipment and environments such as pump stations, gates, main canals, branch canals, and ditches in each irrigation district can be achieved, supporting image or video formats based on equipment function configuration.
5) Irrigation Water Volume Billing
Through the central station intelligent monitoring system and remote telemetry terminals of each measurement and control station, billing for water usage flow at measurement points such as pump stations, main canals, branch canals, and ditches in each irrigation district is realized, helping users to utilize water resources scientifically and reasonably.
6) Data Statistical Analysis
Through the central station intelligent monitoring system, statistical and analytical data on water levels, flow, and water volume at measurement points such as pump stations, main canals, branch canals, and ditches in each irrigation district can be achieved, including maximum, minimum, average, and cumulative values of various data for statistical periods such as year, month, ten days, week, day, and hour, helping users manage water resources in the management area and make scientific and reasonable decisions.
7) Data Forecasting and Alarming
Data Forecast: The system achieves operational data forecasting management and automated control based on historical data, equipment status, and operational trend curves through necessary parameter settings, realizing the informationization and intelligent management of the irrigation district system.
Abnormal Alarm: Based on various data information collected from each measurement and control station in the irrigation district, the system automatically analyzes and judges, and will automatically voice alarm if data exceeds limits or equipment anomalies occur, reminding users to check and handle in a timely manner.
8) Intelligent Water Supply Scheduling
Through the central station intelligent monitoring system, based on the statistical and analytical data of water levels, flow, and water volume at measurement points in each irrigation district, an optimized water supply scheduling plan can be calculated. The system can automatically control the water supply amount and time for each irrigation district, helping users optimize the utilization of water resources.
9) Mobile Monitoring Management
The system supports mobile APP services, enabling monitoring of water levels, flow, water volume, water fees, and other data, as well as equipment and video monitoring at measurement points such as pump stations, main canals, branch canals, and ditches in each irrigation district. This allows users to monitor and manage measurement and control stations in each irrigation district anytime and anywhere.
10) System Security Management
The system is designed with functions such as data management, station management, user management, Password management, project management, and Sign In.
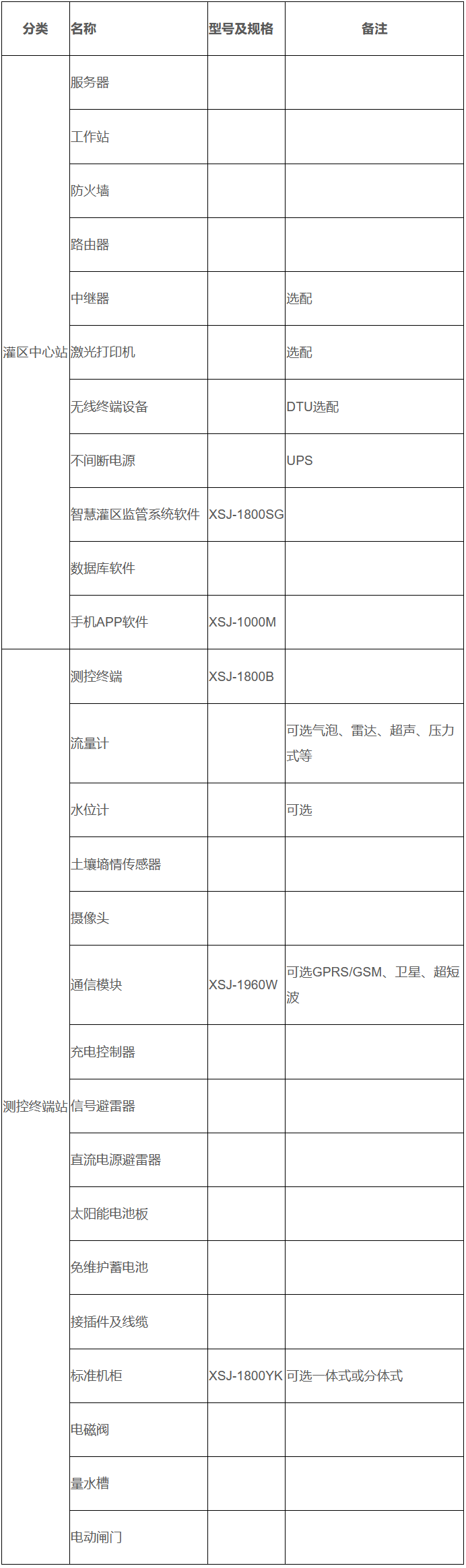
The smart irrigation area supervision system equipment will have different equipment configurations, installation requirements, and system integration application methods based on the project's construction or renovation scope, scale, technical requirements, and investment. The following is only a reference for the selection of equipment for the smart monitoring system of irrigation areas.
Typical equipment configuration of the smart monitoring system for irrigation areas
Previous:
The next one: