Reservoir Flood Forecasting and Dispatching System
- Overview
- Main Features
- Main Indicators
- Main functions
- Device Configuration
The reservoir flood forecasting and dispatching system is suitable for medium and large reservoirs, hydropower plant reservoirs, etc. The reservoir flood control is used to intercept and store flood peaks or to stagger them, and it is used in conjunction with the automatic monitoring and reporting system for rainfall and water conditions in the watershed reservoirs and the safety monitoring system for reservoir dams. It is designed to adapt to the natural characteristics of the watershed and the laws of runoff generation and convergence, creating flood forecasting and dispatching models. By calculating and processing real-time received rainfall data and inflow and outflow water level and flow information, it achieves real-time flood forecasting and automatically forms flood control dispatch plans, presenting a unified information platform to the user interface in the form of graphics, curves, and data tables.
The application of the reservoir flood forecasting and dispatching system is beneficial to prevent or avoid flood disasters in watershed reservoirs, reduce operational management costs, improve the safe operation of user reservoirs, and enhance the efficiency of overall flood management and the level of optimized utilization of reservoir water resources.
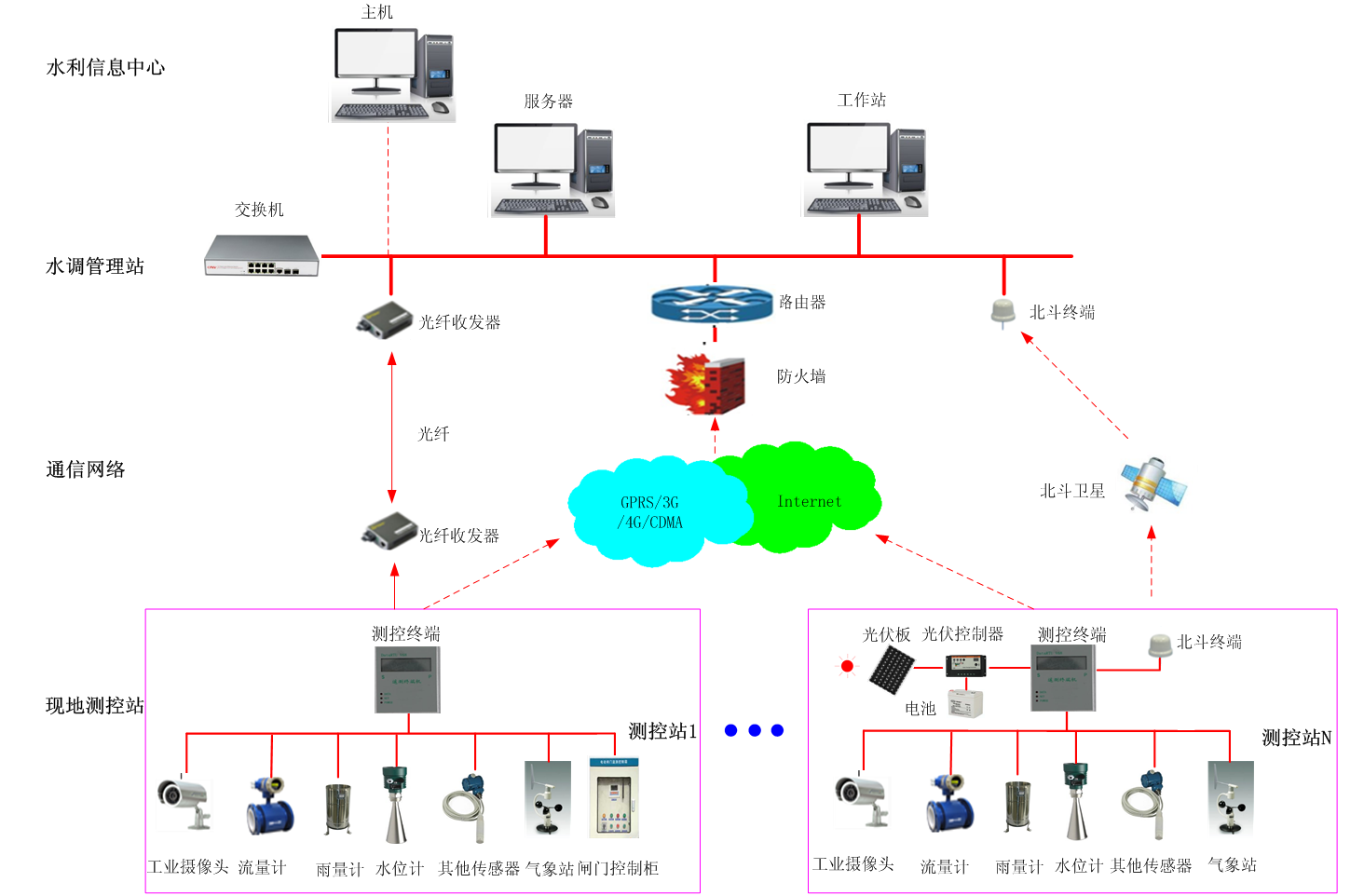
Network diagram of the reservoir flood forecasting and dispatching system.
1) The system software adopts an integrated design of graphics, models, and libraries; the flood forecasting uses advanced models, resulting in high forecasting accuracy.
2) Based on the hydrodynamic model of the reservoir and geographic information system, a multi-objective comprehensive optimal solution is conducted to generate reservoir scheduling plans, including water levels before and after water transfer, changes in water levels, water transfer times, leakage losses, etc. The water regulation control is practical and effective.
3) The system has complete functions, a user-friendly interface, is practical and convenient, and meets the requirements of water conservancy and water regulation standards.
4) An intelligent water regulation system platform is adopted, which can provide intelligent decision-making solutions for reservoir scheduling based on the natural characteristics of the watershed and the laws of production and runoff, utilizing big data analysis of reservoir water resources to guide actual scheduling.
1) Operating environment parameters
Ambient temperature: -20 to 50℃, allowable relative humidity: ≤90%
2) Measurement error of parameters: ≤±0.5% (depends on the selected acquisition sensor)
3) Control accuracy: 100%
4) Electrical quantity acquisition cycle: ≤1s
5) Non-electrical quantity acquisition cycle: ≤1s
6) Status and alarm point acquisition cycle: ≤500ms
7) Event record resolution time: ≤2ms
8) Pump/gate LCU data transmission time to real-time database: ≤1s
9) Pump/gate LCU response time to control command: ≤1s
10) System response time for calling a new screen: ≤1s
11) Dynamic data refresh time on displayed screen: ≤1s
12) Main control level control function response time: ≤1s
13) Time from alarm or accident occurrence to sound output on screen: ≤2s
14) System availability: ≥99.9%
15) Mean time between failures (MTBF): 60000 hours
1) Flood Forecast
l Timed automatic forecasting (automatically forecast once every hour), using rainfall and water level station telemetry values within the basin for automatic forecasting and automatic storage. Rolling timed forecasts at any whole hour based on real-time corrected flood processes at the measurement stations.
l Automatic correction of forecasts, if errors or omissions are found in the hydrological data used for forecasting, the latest information, manual interpolation, and corrected rainfall and water level values can be used to re-make forecasts, which can overwrite the original forecast results.
l The water level and flow curves of various hydrological stations within the basin can be modified to ensure that the updated water level and flow relationship curves can timely participate in flood forecasting.
l Trial forecasting allows manual input of rainfall amounts for a specific period to conduct flood forecasting.
l Forecast results can be counted, queried, exported, printed, etc. Online and offline forecasting can be achieved.
2) Flood Dispatching
l Simulation dispatching: Using water levels, forecasts and actual flood processes, actual gate operation processes, and historical dispatching data such as power generation flow for dispatching calculations, summarizing and analyzing the simulation dispatching process.
l No flood discharge mode: Calculate the water level process based on the current reservoir water level and the forecasted inflow process.
l Dispatching regulation mode: Operate according to the current reservoir water level and forecasted inflow, following the reservoir's flood control dispatching regulations, generating flood control dispatch plans for the reservoir.
l Forecast pre-discharge mode: Based on reliable short-term flood forecasts, the reservoir can open gates in advance to release water to free up storage capacity for the upcoming flood. Especially when the reservoir water level is above the flood control limit.
In special conditions where the water level is above the flood control limit, it is necessary to lower the reservoir water level below the flood control limit before the flood arrives, quickly determining the gate opening time, gate opening composition, discharge flow, and the moments below the flood control limit during the flood forecast period.
l Gate control and tail flood retention mode: Based on the inflow flow process, output plan, and gate opening and closing plan during the dispatching period, perform flood regulation calculations starting from the initial water level on an hourly basis. Through calculations, the opening and closing times of the gates can be determined, as well as the rebound water level after closing the gates.
l Water regulation results can be counted, queried, exported, printed, etc. It supports online calculations and offline calculations.
3) Water Level Status Monitoring
Graphically display the current water level, indicate warning water levels and danger water levels, and dynamically show the changes in the current water level.
4) Real-time Water Condition Monitoring
Real-time water condition list display, comparing the current water level with warning and danger water levels to achieve water condition monitoring and early warning; detailed water condition curve graphs can be queried for measurement points, showing annual, monthly, daily, hourly water levels, etc., to understand the trend of water level changes.
5) Water Condition Data Analysis
Comparative analysis of historical water conditions at monitoring points over the years, months, and days, supporting multiple curves displayed on the same screen.6) Flow Collection Analysis
The system calculates the flow of the measurement point by monitoring water level information and structuring flow rate calibration curves, facilitating the management of flow data.
7) Rainfall Data Monitoring
Query the annual, monthly, daily, and hourly rainfall bar charts of measurement points in the area. When rainfall exceeds the heavy rain level, it will be highlighted in red for warning display.
8) Early Warning Information Release
Based on monitoring data and set alarm thresholds, early warning releases are made. The warning levels are divided into: Good (green), Dangerous (red), High Risk (yellow), and the warning information is simultaneously sent to relevant personnel's Mobile APP.
9) Flood Control Plan Processing
Based on the released warning levels, orderly emergency processing is formed for communities, schools, hospitals, factories, and warehouses affected by easily accumulated water, flooding points, and dangerous river sections. Hazard information is quickly released to notify responsible persons, avoiding and reducing losses of life and property.
10) Archive Information Management
Establish archive information for monitoring equipment installed at monitoring points for easy system maintenance. A contact information database can be established for areas with high hazard indices, drainage pump stations, gate stations, and factory managers.
11) System Security Management
Manage the settings of parameters related to the automated flood control dispatching system of the reservoir. This includes user management, reservoir settings, system menu customization, and system parameter settings.
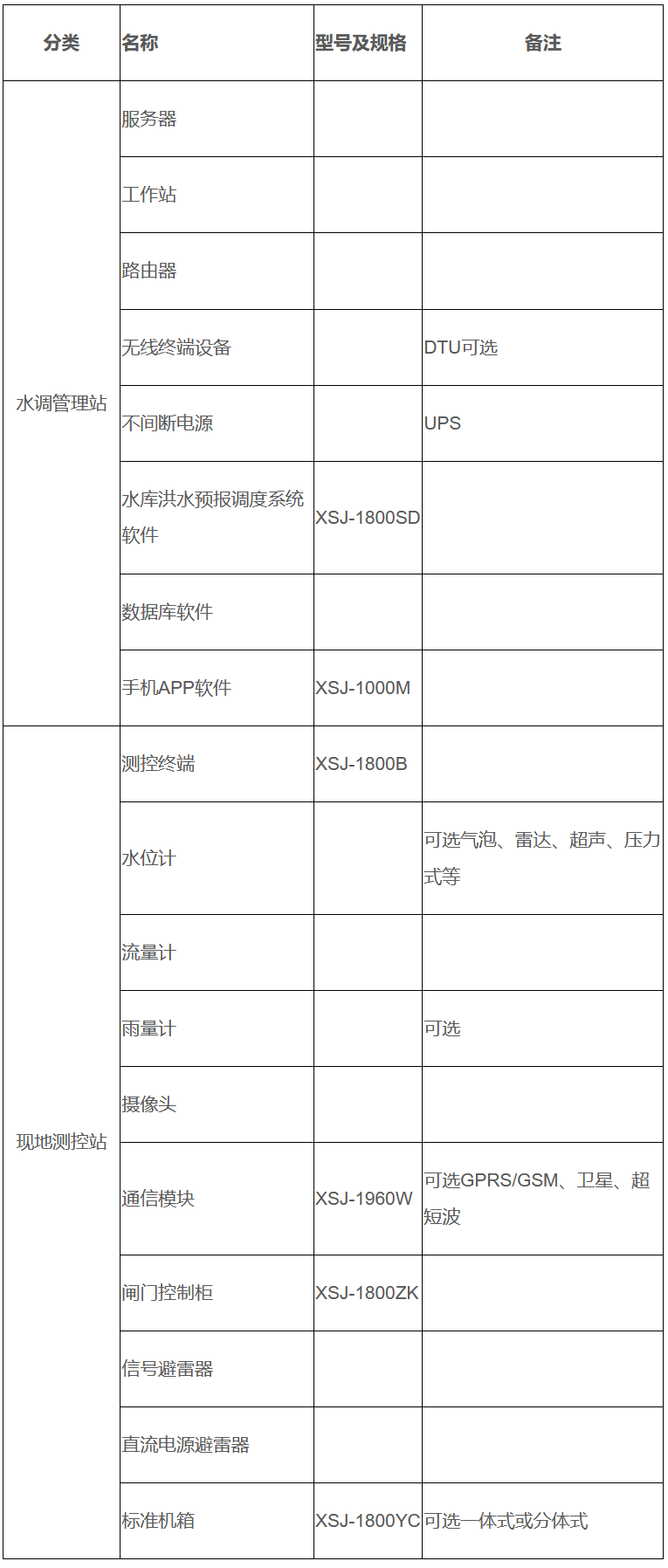
The reservoir flood forecasting and dispatching system equipment will have different equipment configurations, installation requirements, and system integration application methods based on the project's construction or renovation scope, scale, technical requirements, and investment. The following is only a reference for the selection of equipment for the reservoir flood forecasting and dispatching system.
Typical equipment configuration of the reservoir flood forecasting and dispatching system
Previous: